This section is designed to help our users understand and use our data better. It will explain how everything on UDRP.Tools works.
If you're looking for detailed information about our data, please check our Notes on Data.
Unregistered users have a quota of five searches per day.
Registering an account on the site is free. Registering on the site creates an account with 50 non-expiring search credits. These are available whenever the daily allocation of five searches is exceeded.
Registered users are able to purchase additional blocks of non-expiring search credits.
The homepage (Search) is the main interface our users see. There are two primary components to the search interface: Filter Cases and The Results. The Filter Cases section is on the left side and allows users to filter and search for cases meeting particular criteria. The Results are where the cases matching the criteria are found. The domain, case (link to full case details), date and decision type are returned with all results.
Search filters are grouped up into three tabs: Text, Parties and Domain. These group different search functionality based on the type of data that will be searched.
Keyword Search - Entering the keyword will find decisions in which the keyword appears.
Example: BLUE
Multiple Keyword Search - Searching on multiple keywords will only return decisions in which all the keywords appear somewhere in the decision.
Example: BLUE RED
Exact Match Search - Entering a phrase in quotes, will return only those decisions where that phrase appears.
Example: "BLUE RED"
Exclude Keyword Search - Use the minus sign - to exclude keywords.
Example: BLUE -RED - This search would include blue but exclude results with the keyword red.
Example 2: +BLUE -RED - This search is functionally identical. You can tell the search to require a keyword with the + symbol.
Wildcard Search - Use * to perform wildcard searches.
Example: IDENT*
This will return decisions that contain the words IDENTITY, IDENTICAL, IDENTIFY, etc.
Wildcards do not work with "exact match" searches, but can be used in combination with them.
Example (invalid): "is confus*" - This won't work
Example (valid): "domain is" confus* - This will match anything with "domain is" and any string starting with confus
Proximity Search - Proximity searches enable you to search for one keyword within a certain number of words of a second keyword.
To search for two words appearing within a certain number of words of each other in any order: word1~number~word2
For example, researching how panelists treat late filed responses is a task for which proximity search may be helpful. Without a proximity search, it could be difficult to identify those cases. Many such cases would not include the exact match phrase "late response", while doing a broad search for the words "late" and "response" appearing anywhere in the decision would result in too many false positives.
A proximity search for decisions where the word "late" appears within five words of the word "response" would successfully locate permutations such as "response was late", "late filed response" and "response was filed one day late".
To perform this search, enter: late~5~response.
Ignored words and punctuation
Some words, such as “the”, “in”, etc. are ignored. These are called “stop words”. A full list of stop words is below
One, two and three letter words are also ignored.
For example, a search on the exact phrase “be the best”, will be treated as a keyword search on “best”
Punctuation, such as commas and periods are ignored
Capitalization does not matter
Deep Search
Deep Search is available to logged in users. If Deep Search is selected, the exact text entered into the search box will be matched against the raw text of the decision. There are no stop words in Deep Search.
For instance, if you wish to search on the phrase “this is what”, it will not work in the regular search since THIS, IS and WHAT are all stopwords.
By selecting the Deep Search option and entering THIS IS WHAT in the keyword search box, UDRP.tools will return decisions that include the exact phrase “THIS IS WHAT” in the decision text.
Deep Search is much slower than regular search.
Filter tags appear in little “pills” above the search results. Filter tags are helpful to confirm the terms used to refine the search. You can also click on a pill to remove that filter from the search results.
For instance, if a search is performed using the conditions:
The Filter Tags will look as follows:

If you want to remove the requirement that only Denied decisions appear in the results, just click on the  button. This will eliminate that filter and will automatically rerun the search, displaying the search results for a search with the conditions:
button. This will eliminate that filter and will automatically rerun the search, displaying the search results for a search with the conditions:
As follows-

This section shows frequency tables about Panelists and Decisions. Custom Frequency information also appears here if selected. These results are all clickable and filter for the selection clicked and is automatically added to the current search.
There are also two clickable Reports. Show Citations Report, which shows which are the most popular cited cases for the current search. Show Outcomes Report by Panelist which is a visual representation of the distribution of decisions of the top 25 most frequent panelists in the current search.

Panelist Research homepage is a simple page to find a panelist. All panelists in our database are listed and searchable.
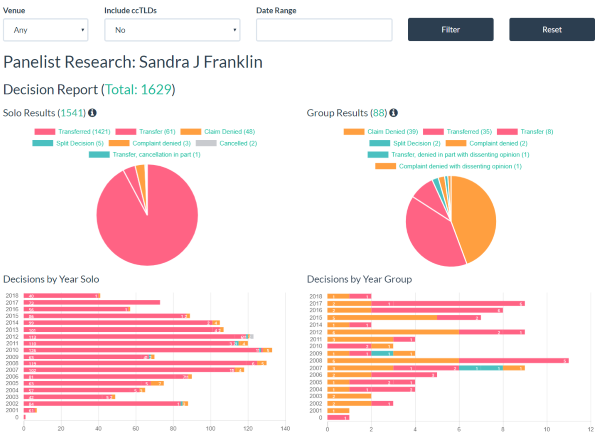
Panelist profiles allow you to see a breakdown of the decisions of any panelist and do some basic filtering based on venue, including ccTLDs, and date range.
The report shows solo results, where the panelist was the sole panelist, and group results, where the panelist was a member of a three party panel. Our data is broken down by decision types and decision types by year for both solo and group results.
The Panelists Served With information lets you see how a panelist has interacted with other panelists in group situations based on decision outcomes.
Citations Used shows which cases the panelist most frequently cites in their decisions in both solo and group situations.
Citations are used throughout UDRP Tools. They can be found on specific cases, panelist profiles and special citation related pages. The special citation related pages are:
Every case has a page that displays the information we have collected from the source. All data is collected from the respective venue. Some fields are normalized to a certain standard.
Some cases may have additional meta information: